What you must know about virtual reality VR
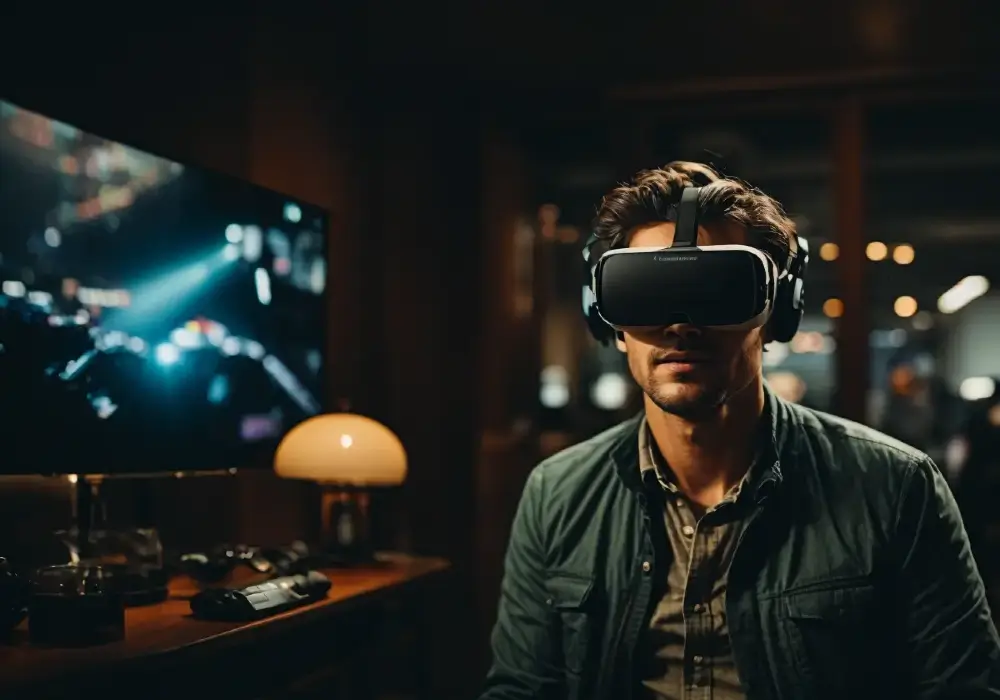
Virtual Reality (VR) refers to the use of computer technology to create an immersive simulated environment that can be experienced as if it were real. In recent years, VR has become increasingly popular and has been adopted in various industries, including gaming, education, healthcare, and entertainment. Here are some specifics :
Advantages:
- Immersive Experience: Virtual reality provides an immersive experience that allows users to feel as though they are actually present in a simulated environment. This can enhance learning, training, and entertainment experiences.
- Increased Engagement: VR can increase engagement by creating a more interactive experience that encourages users to explore and interact with virtual environments in ways that are not possible in the real world.
- Safe Training Environment: Virtual reality can create a safe and controlled training environment, which is especially useful for training in high-risk industries such as aviation, medicine, and military.
- Cost-Effective: VR can be a cost-effective solution for training and education, as it eliminates the need for physical training equipment, travel, and other associated costs.
Disadvantages:
- Expensive: The cost of VR technology can be a significant barrier to adoption, especially for individuals and small businesses.
- Health Risks: Prolonged use of VR can cause health issues such as motion sickness, eye strain, and headaches.
- Limited Interaction: Virtual reality can be isolating, as users are cut off from the real world and limited in their ability to interact with others in the real world.
- Limited Realism: While VR technology has come a long way, it still has limitations in terms of realism, which can limit its usefulness in certain applications.
Overall, virtual reality has many potential benefits but also has its drawbacks. Understanding these advantages and disadvantages is important in determining whether or not virtual reality is the right solution for a particular application or use case.
The basic principle behind virtual reality is to create a three-dimensional environment that mimics the real world. This is accomplished through the use of sensors, displays, and input devices that work together to simulate the user’s physical presence in a virtual environment.
To create a virtual reality experience, the first step is to capture real-world data. This can be done through a variety of methods, such as 3D scanning or photogrammetry, which create a digital representation of real-world objects and environments.
Once the data is captured, it is processed by a computer to create a virtual environment. This involves creating 3D models of the objects and environments, and programming the behavior and interactions of the elements within the virtual environment.
The virtual environment is then displayed to the user using a specialized display device, such as a VR headset or projection system. These displays typically include two screens, one for each eye, which creates a 3D effect when viewed through the lenses of the headset.
To track the user’s movement within the virtual environment, sensors are used to detect the user’s position and orientation. This allows the virtual environment to adjust in real-time to the user’s movements, creating a more immersive and realistic experience.
In addition to visual and movement tracking, virtual reality systems also include input devices that allow users to interact with the virtual environment. This can include handheld controllers, haptic feedback devices, and even full-body motion tracking systems.
Overall, virtual reality is a complex and sophisticated technology that combines hardware, software, and user input to create a truly immersive and interactive experience. As the technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more advanced and realistic virtual reality experiences in the future.
The main components of a VR system are:
- Input devices: Input devices allow users to interact with the virtual environment. These can include handheld controllers, haptic feedback devices, and full-body motion tracking systems. They are designed to simulate the actions that users would perform in the real world, such as reaching out to touch objects, grabbing and moving them, and using tools or weapons.
- Display devices: Display devices are used to present the virtual environment to the user. They typically consist of a high-resolution screen or screens, which are mounted within a headset or projection system. The screens are positioned in front of the user’s eyes and display stereoscopic images, creating a 3D effect that simulates depth perception.
- Tracking sensors: Tracking sensors are used to monitor the user’s movements and position within the virtual environment. These sensors can include cameras, gyroscopes, accelerometers, and other motion detection technologies. They are used to track the user’s head and body movements, as well as the position and orientation of the input devices.
- Processing unit: The processing unit is responsible for running the software that creates the virtual environment and manages the input and output of data. This includes rendering the 3D models, simulating physics and other environmental effects, and processing the input from the tracking sensors and input devices. The processing unit can be a standalone device, such as a gaming console or PC, or it can be integrated into the headset or other components of the VR system.
When these components work together, they create an immersive and interactive virtual environment that simulates the real world.